Skontaktuj się z koordynatorem
+48 75 645 2024
Napisz do nas wiadomość
urologia@kcmclinic.pl
Varicocele surgery
Varicocele is a vascular disorder characterized by anomalous dilatation, elongation, and curvature of the veins within the seminal vein (Fig. 1). This condition gives rise to pain, discomfort, and a gradual impairment of testicular function. Furthermore, scientific data indicate that varicocele has emerged as a prevalent factor contributing to male infertility. The prevalence of varicocele exhibits a range of 10 to 15% among males, while infertile males demonstrate a higher range of 19 to 41%. Research has demonstrated that the presence of varicocele in the spermatic cord adversely impacts various aspects of sperm quality, including concentration, motility, and morphology. Furthermore, varicocele can compromise the integrity of sperm DNA.
As a result of the lack of clear and definitive symptoms, patients frequently do not receive a timely diagnosis, which can subsequently result in decreased spermatogenesis in certain male individuals.
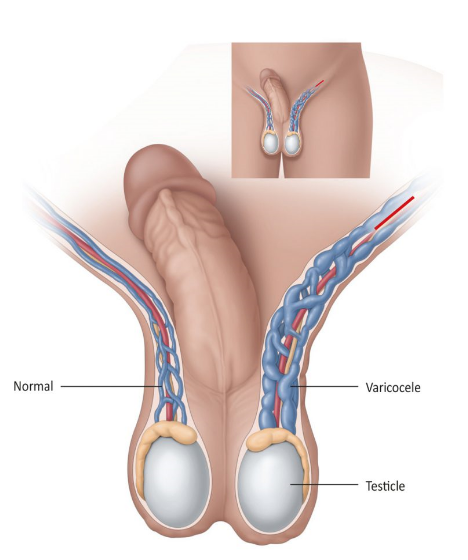
The etiology of varicocele
The etiology of varicocele remains incompletely understood. According to certain studies, there is a belief that the onset of the condition could perhaps be linked to the rapid development of the genitalia in adolescent males. The etiology of varicocele is postulated to be attributed to the presence of malfunctioning valves within the veins located in the scrotal region, specifically positioned directly above the testes. Typically, these valves are responsible for regulating the circulation of blood to and from the testes. In instances where the regular circulation pattern is disrupted, blood retracts, resulting in the dilation (enlargement) of the veins. This phenomenon predominantly manifests during the stage of adolescence known as puberty. Varicocele predominantly manifests in the vicinity of the left testicle in roughly 85% of instances.
Varicocele leading to compromised blood circulation can result in elevated testicular blood temperature, potentially leading to detrimental effects on sperm viability and production.
There are three distinct levels of severity when it comes to varicocele:
- detectable through palpation only during physical activity;
- detectable through palpation even during periods of repose;
- noticeable from a distance without the need for a physical examination.
Symptoms of varicocele
The majority of patients remain uninformed about the existence of varicocele unless they give rise to issues with fertility or are identified during a regular medical examination. Persistent aches or a feeling of heaviness in the testicles, are associated with the presence of varicocele. These symptoms tend to worsen during the day, particularly in warm conditions or following physical exertion. Frequently, patients may experience or observe dilated veins in the scrotum and a reduced size of the testicular nucleus adjacent to the varicocele.
Varicocele has the potential to induce spasms in a diseased testicle, which mostly comprises tubules responsible for sperm production. In instances of injury, such as in the context of varicocele, the nucleus undergoes contraction and softening.
Infertility is a potential consequence of varicocele in males, as it may result in reduced spermatogenesis. However, it is important to note that not all boys with varicocele will experience fertility issues later in life.
Trteatment of varicocele
The necessity for treatment of varicocele arises primarily in instances of infertility or when the problem elicits enduring pain and discomfort.
In recent years, surgical treatment, particularly micro-surgical excision, has emerged as the prevailing approach for managing varicocele. The utilization of micro-surgical varicose vein excision has been found to have a positive impact on multiple parameters of semen quality, such as concentration, motility, and sperm morphology.
The postoperative pain is often light, and it is common for patients to resume their regular activities within two days following the surgical procedure. It is postulated that approximately 50% of males who have surgical intervention to eliminate varicocele in the spermatic cord have the potential to achieve biological parenthood.
The process of diagnosing varicocele involves several steps. Firstly, a thorough medical history is obtained from the patient, including any symptoms experienced and any family history of varicocele. A physical examination follows this when the healthcare
A comprehensive medical assessment is important to ascertain or validate the existence of varicocele in the individual. Varicocele typically reduces the size of the nucleus. Most of the time, scrotal ultrasonography imaging is used to prove that blood is flowing backward in the veins of the enlarged testicles.
The postoperative guidelines for scrotum surgeries are comparable to those for other similar procedures. These recommendations encompass restrictions on physical activity, the administration of pain medication, and the application of cold compresses. The typical duration for complete resumption of activity is generally observed to be between 2 and 3 weeks. However, it is noteworthy that a majority of males are capable of returning to sedentary occupational tasks within a span of 24 to 72 hours.
Dr. Alam Bouhaouli at KCM Clinic performs surgical interventions for varicocele.
Bibliography:
- Cauni, V., Ciofu, I., Stoica, C., Balescu, I., Bacalbasa, N., & Persu, C. (2022). Doppler Ultrasonography – An Important Tool in Managing Patients With Varicocele and Secondary Infertility. In Vivo, 36(5), 2392-2399. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/36099105/
- Morini, D., Spaggiari, G., Daolio, J., Melli, B., Nicoli, A., Feo, G. D., Valli, B., Viola, D., Garganigo, S., Magnani, E., Pilia, A., Polese, A., Colla, R., Simoni, M., Aguzzoli, L., Villani, M. T., & Santi, D. (2021). Improvement of sperm morphology after surgical varicocele repair. Andrology, 9(4), 1176-1184. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33825345/
- Zhang, X., Deng, C., Liu, W., Liu, H., Zhou, Y., Li, Q., Zheng, H., Wang, Q., Jiang, M., Pang, T., Ma, C., Huang, C., Zhao, Q., & Tang, Y. (2022). Effects of varicocele and microsurgical varicocelectomy on the metabolites in semen. Scientific Reports, 12. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/35338186/
Netography:
- Varicocele, https://patients.uroweb.org/other-diseases/varicocele/, [access: 01.09.2023].
- Varicocele: Symptoms, Treatment, Diagnosis, https://www.uclahealth.org/medical-services/urology/varicocle-symptoms-treatment-diagnosis, [access: 01.09.2023].


